
In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, one website stands as a beacon for enthusiasts, learners, and innovators venturing into the dynamic realm of medical robotics – TechnologyRefers. As the virtual gateway to the future of healthcare, this platform is a reservoir of knowledge, dedicated to unraveling the complexities and potentials of medical robots that are reshaping the way we approach healthcare.
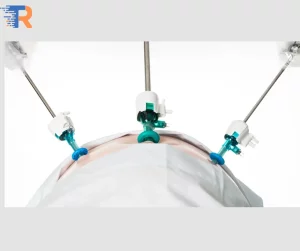
Embarking on a Robotic Odyssey:
At the heart of TechnologyRefers lies an unwavering commitment to exploring the depths of the medical robotic world . The platform serves as an interactive guide, ushering users through the intricacies of this transformative field. Whether one is a seasoned medical professional or an aspiring student, TechnologyRefers offers a comprehensive journey into the applications, advancements, and nuances of medical robots that are revolutionizing patient care and healthcare practices worldwide.
Comprehensive Medical Robots Information:
TechnologyRefers serves as a digital oasis for those thirsty for knowledge about medical robots. The website’s unreserved library encompasses a broad selection of information, from the basics of robotic-assisted surgery to the particulars of robotic prosthetics and rehabilitation. Guests can explore into the world of robotic exoskeletons, telepresence robots for healthcare, and the latest innovations in diagnostic robotics. With comprehensive articles, and case studies, the platform caters to all levels of proficiency, nurturing a community of learners passionate about the connection of technology and healthcare.
Learning the Art of Medical Robotics:
One of the standout features of TechnologyRefers is its commitment to education in the field of medical robotics. Recognizing the transformative potential of this technology, the platform goes beyond information dissemination, providing a structured pathway for individuals to learn medical robotics . From introductory courses to advanced modules, TechnologyRefers ensures that aspiring roboticists and healthcare professionals can acquire the necessary skills to navigate this dynamic and evolving field.
Balancing the Scales: Benefits and Drawbacks of Medical Robots:
As a hub for comprehensive information, TechnologyRefers engages in candid discussions about the benefits and drawbacks of medical robots . The platform recognizes the immense potential of these robotic marvels in improving surgical precision, reducing recovery times, and enhancing overall patient outcomes. Simultaneously, it delves into the ethical considerations, potential job displacement concerns, and the imperative for robust cybersecurity measures in the realm of medical robotics. By presenting a balanced view, TechnologyRefers empowers its audience to critically evaluate the role and impact of medical robots in the healthcare ecosystem.
Navigating the Cost Landscape:
Understanding the financial landscape is crucial in the adoption of any technology, and medical robotics is no exception. TechnologyRefers provides a nuanced exploration of the cost considerations associated with medical robots. From the initial investment in robotic surgical systems to the long-term operational costs and potential savings in healthcare delivery, the platform offers insights that are invaluable for healthcare administrators, policymakers, and investors navigating the decision-making process.
Beyond Information: A Community of Innovators:
TechnologyRefers is not just a repository of information; it’s a thriving community of innovators, practitioners, and enthusiasts passionate about the fusion of technology and healthcare. The platform hosts forums, webinars, and collaborative projects that encourage meaningful discussions and knowledge exchange. As medical robotics continues to advance, TechnologyRefers stands as a dynamic hub where ideas are born, connections are made, and the future of healthcare is shaped.
Paving the Way to a Healthier Tomorrow:
In conclusion, TechnologyRefers emerges as a trailblazer, paving the way for a healthier tomorrow through its exploration of the medical robotic world. From learning the intricacies of robotic-assisted surgery to navigating the ethical considerations surrounding these technological marvels, the platform is a compass for those venturing into the future of healthcare. As medical robotics becomes an integral part of the healthcare landscape, TechnologyRefers not only informs but inspires a collective journey towards a future where technology and compassion intersect, revolutionizing patient care and redefining the possibilities within the medical world.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
Robotic Surgery Procedures: Precision Redefined in the Operating Room
In the landscape of modern medicine, Robotic Surgery Procedures represent a revolutionary paradigm, where precision meets innovation in the operating room. These procedures involve the use of robotic systems, controlled by skilled surgeons, to perform intricate surgeries with enhanced accuracy. From minimally invasive surgeries to complex interventions, robotic surgery procedures have redefined the boundaries of surgical capabilities, offering patients the benefits of reduced scarring, quicker recovery times, and improved outcomes.
Future of Medicine Dispensing: Automating Healthcare with Innovation
The Future of Medicine Dispensing is undergoing a transformative shift, propelled by automation and advanced technologies. Automated Medication Dispensing Machines are emerging as key players in this evolution, streamlining medication management in healthcare settings. These machines ensure accuracy in dosage, reduce the risk of human error, and enhance efficiency in medication distribution. As we glimpse into the future, these automated dispensing solutions stand at the forefront of a healthcare landscape where precision and technological integration redefine patient care.
Automated Medication Dispensing Machine: Redefining Medication Management
The Automated Medication Dispensing Machine is a cornerstone in the evolution of healthcare delivery, providing a sophisticated solution to medication management. These machines, often set up in hospitals and healthcare services, automate the dispensing process, dipping the possible for errors and improving the overall effectiveness of medication management. With features such as barcode scanning, inventory tracking, and user authentication, these machines not only improve patient protection but also put in to the optimization of healthcare workflows.

399$ Dental Implants: Making Dental Care Accessible
The advent of 399$ Dental Implants signifies a revolutionary stride towards making dental care more accessible and affordable. Traditionally considered a costly dental procedure, the introduction of budget-friendly dental implants at $399 opens doors for a broader demographic to benefit from this transformative treatment. This innovation not only addresses the financial barriers associated with dental implants but also contributes to the democratization of quality dental care, ensuring that more individuals can enjoy the benefits of permanent and aesthetically pleasing tooth replacement.
Globus Robotic Spine Surgery: Precision in Spinal Interventions
Globus Robotic Spine Surgery represents a leap forward in spinal interventions, where robotics and precision converge to address complex spinal conditions. This advanced robotic system allows surgeons to plan and execute spinal procedures with unparalleled accuracy. From spinal fusions to decompressions, the Globus Robotic Spine Surgery system enhances the surgeon’s capabilities, resulting in improved patient outcomes, reduced recovery times, and minimized disruption to surrounding tissues.
ExcelsiusGPS Surgical Navigation: Navigating Surgical Precision
In the realm of surgical navigation, ExcelsiusGPS Surgical Navigation stands as a beacon of precision, guiding surgeons with advanced technologies during procedures. This robotic navigation system combines imaging, robotics, and real-time feedback to enhance the accuracy and safety of surgical interventions. Surgeons can use ExcelsiusGPS for a range of procedures, from spinal surgeries to joint replacements, ushering in a new era where technology becomes an indispensable ally in achieving surgical excellence.
Cambridge Medical Robotics CMR Surgical: Pioneering Minimally Invasive Surgery
Cambridge Medical Robotics (CMR Surgical) is at the forefront of advancing minimally invasive surgery with robotic assistance. The company’s robotic system is planned to improve the capabilities of surgeons, enabling them to perform difficult procedures through smaller incisions. With the ambition of improving patient outcomes and dropping the crash of surgery on the body, CMR Surgical contributes to the constant progression of surgical techniques and technologies.
Mako Surgical and Stryker Mako: Transforming Orthopedic Surgeries
In the realm of orthopedic surgeries, Mako Surgical and Stryker Mako have become synonymous with transformative precision. The Mako system, developed by Stryker, utilizes robotic technology to assist surgeons in planning and executing orthopedic procedures with exceptional accuracy. From knee replacements to hip surgeries, Mako Surgical and Stryker Mako systems exemplify the fusion of robotics and orthopedic expertise, offering patients personalized and precise solutions for joint health.
Da Vinci Surgical System and Da Vinci Robotics: Mastering Surgical Precision
The Da Vinci Surgical System and Da Vinci Robotics have become iconic in the field of robotic-assisted surgery. Developed by Intuitive Surgical, the Da Vinci system allows surgeons to perform minimally invasive procedures with enhanced dexterity and visualization. From gynecological surgeries to prostatectomies, Da Vinci Robotics has redefined the landscape of surgical precision, enabling surgeons to navigate complex anatomies with unparalleled control and precision.
Robotic Assisted Surgery: Elevating Surgical Capabilities
Robotic Assisted Surgery is a transformative approach that elevates surgical capabilities by integrating robotic systems into traditional surgical procedures. These systems offer surgeons with improved visualization, dexterity, and precision, most important to improved patient outcomes and reduced healing times. Robotic-assisted surgery spans a variety of specialties, as well as urology, gynecology, and general surgery, signifying the flexibility and impact of robotics in enhancing the surgical experience.
ROSA Robotics and Telesurgery: The Convergence of Robotics and Connectivity
ROSA Robotics exemplifies the convergence of robotics and connectivity in the realm of neurosurgery. This robotic system assists neurosurgeons in planning and executing intricate procedures with precision. The integration of telesurgery capabilities allows remote collaboration and guidance, enabling experts to contribute to surgeries from different locations. ROSA Robotics and telesurgery redefine the boundaries of neurosurgical interventions, opening avenues for global collaboration and expertise exchange.
Robots in Medical Field: Shaping the Future of Healthcare
The presence of Robots in the Medical Field signifies a paradigm shift in healthcare delivery. From surgical assistants to rehabilitation companions, robots are increasingly becoming integral components of the medical ecosystem. Their applications expand to diagnostics, therapy, and patient care, showcasing the varied ways in which robotics is determining the future of healthcare. As technology continues to proceed, the role of robots in the medical ground is hovering to enlarge, causative to more competent, accurate, and patient-centric healthcare solutions.
Robotics in Pharmaceutical Industry: Transforming Drug Development and Production
In the Pharmaceutical Industry, the integration of robotics is transforming drug development and production processes. Robotic systems play a crucial role in laboratory automation, sample handling, and high-throughput screening, accelerating the pace of drug discovery. From robotic liquid handlers to automated packaging systems, robotics in the pharmaceutical industry enhance efficiency, accuracy, and reproducible, laying the foundation for innovative and streamlined approaches to drug manufacturing.
In conclusion, the fusion of robotics with various aspects of medical care is propelling healthcare into a new era of precision, accessibility, and innovation. From robotic surgery procedures that redefine surgical precision to the transformative impact of automated medication dispensing machines, each keyword represents a unique facet of how technology is reshaping the landscape of medicine. As we navigate this intersection of robotics and healthcare, the future promises not only advancements in technology but also a redefined standard of care that prioritizes precision, accessibility, and improved patient outcomes.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
Benefits and Drawbacks of Medical Robots
| Benefits of Medical Robots | Drawbacks of Medical Robots |
|---|---|
| 1. Precision in Surgical Procedures: Medical robots offer unparalleled precision in surgeries, leading to improved outcomes. | 1. High Initial Cost: The acquisition and installation of medical robotic systems can incur substantial upfront costs for healthcare institutions. |
| 2. Minimally Invasive Procedures: Robots enable minimally invasive surgeries, reducing patient trauma, pain, and recovery times. | 2. Maintenance Expenses: Ongoing maintenance and servicing of robotic systems contribute to additional expenses for healthcare providers. |
| 3. Enhanced Visualization: Medical robots provide surgeons with enhanced 3D visualization, improving their ability to navigate complex anatomies. | 3. Learning Curve: Training healthcare professionals to operate and integrate medical robots into procedures requires time and resources. |
| 4. Reduced Human Error: Automation reduces the risk of human error in surgeries, enhancing patient safety. | 4. Dependency on Technology: Reliance on robotic systems introduces a level of dependency that may pose challenges in emergency situations or system failures. |
| 5. Increased Access to Specialized Care: Robots facilitate telemedicine, allowing experts to remotely assist in surgeries, increasing access to specialized care. | 5. Limited Haptic Feedback: Surgeons may experience limitations in haptic feedback, impacting their tactile perception during procedures. |
| 6. Shorter Recovery Times: Patients undergoing robot-assisted surgeries often experience shorter recovery times compared to traditional methods. | 6. Ethical Considerations: The use of robots in healthcare raises ethical concerns, particularly in decision-making processes and patient interactions. |
| 7. Customization for Patients: Medical robots enable personalized treatment plans tailored to individual patient needs. | 7. Integration Challenges: Integrating robotic systems with existing healthcare infrastructure can pose logistical and compatibility challenges. |
| 8. Remote Monitoring: Robots allow for remote patient monitoring, enhancing postoperative care and follow-up. | 8. Limited Availability: Not all healthcare institutions have access to or can afford the implementation of medical robotic systems. |
| 9. Assistance in Rehabilitation: Robots assist in rehabilitation therapies, aiding patients in regaining mobility and function. | 9. Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to evolving regulatory standards and compliance requirements in the use of medical robots is an ongoing challenge. |
| 10. Faster Surgical Procedures: Medical robots can perform certain procedures more efficiently, reducing surgery duration. | 10. Patient Mistrust: Some patients may express concerns or mistrust towards robotic-assisted procedures, impacting their acceptance. |
| 11. Advancements in Drug Delivery: Robots contribute to advancements in drug delivery systems, improving precision and targeted treatments. | 11. Limited Surgical Specialties: The application of medical robots is more prevalent in certain surgical specialties, limiting their overall scope. |
| 12. Improved Ergonomics: Surgeons benefit from improved ergonomics when using robotic systems, reducing physical strain. | 12. Resistance from Healthcare Professionals: Resistance to adopting robotic technology may arise among healthcare professionals accustomed to traditional methods. |
| 13. Telesurgery Capabilities: Robots enable telesurgery, allowing expert surgeons to perform procedures from remote locations. | 13. Potential Job Displacement: Concerns about job displacement for certain healthcare roles may arise with increased automation. |
| 14. Accessibility in Rural Areas: Remote access to robotic expertise enhances healthcare accessibility in rural and underserved areas. | 14. Cybersecurity Risks: The integration of technology introduces cybersecurity risks that need to be carefully managed. |
| 15. Research and Innovation Catalyst: Medical robots drive research and innovation, pushing the boundaries of healthcare possibilities. | 15. Long Regulatory Approval Processes: Getting regulatory approval for new robotic technologies can be a time-consuming process. |
| 16. Increased Patient Satisfaction: Improved outcomes and reduced recovery times contribute to higher levels of patient satisfaction. | 16. Complexity in Team Collaboration: Collaborative efforts in surgical teams may face challenges due to the complexity of robotic-assisted procedures. |
| 17. Surgical Consistency: Robots ensure consistency in surgical techniques, minimizing variations between procedures. | 17. Environmental Impact: The production and disposal of robotic systems can have environmental implications. |
| 18. Integration with Imaging Technologies: Robots seamlessly integrate with imaging technologies, aiding in accurate preoperative planning. | 18. Resistance to Change: Healthcare institutions may face resistance from staff when transitioning to robotic-assisted procedures. |
| 19. Treatment of Complex Cases: Medical robots enable the treatment of complex cases that may be challenging with traditional methods. | 19. Limited Availability of Training: Adequate training programs for medical professionals in robotic procedures may be lacking. |
| 20. Pioneering Scientific Advancements: The use of medical robots contributes to scientific advancements in the intersection of technology and healthcare. | 20. Perception Challenges: Overcoming skepticism and building public trust in the capabilities of medical robots is an ongoing challenge. |
This table encapsulates the multifaceted landscape of benefits and drawbacks associated with the integration of medical robots in healthcare settings. While highlighting the potential for precision, innovation, and improved patient outcomes, it also addresses the challenges in terms of cost, learning curves, and ethical considerations that accompany the adoption of this transformative technology.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
Historical Background of MR
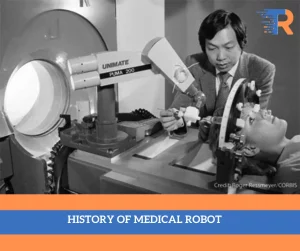
A Journey Through the History of Medical Robotics: Pioneering the Future of Healthcare
The development of medical robotics is a convincing description that intertwines technological modernization, surgical expertise, and a assurance to advancing patient care. The roots of medical robotics can be traced back to the mid-20th century, and the passage has been noticeable by major milestones that have reshaped the background of healthcare.
1950s-1960s: The Early Visionaries
The base of medical robotics was sown in the 1950s and 1960s when visionaries like Dr. John H. Seward envisioned the latent of robotics in surgical actions. Dr. Seward’s work laid the basis for exploring the connection of technology and surgery, setting the stage for future breakthroughs.
1980s: The Birth of Robotics-Assisted Surgery
The 1980s marked a transformative period with the development of the first robotic systems designed to assist surgeons. The PUMA 560 , created by Victor Scheinman, was one such early robotic arm used for delicate surgical procedures. This decade laid the groundwork for the integration of robotics into the surgical realm.
Late 1980s-1990s: Robotic Systems Enter the Operating Room
In 1987, the world witnessed a groundbreaking event as the first documented robotic-assisted surgery took place. The PUMA 560 was utilized in a neurosurgical biopsy, demonstrating the potential for increased precision in delicate procedures. This pivotal moment paved the way for further exploration of robotic applications in various surgical disciplines.
2000s: Da Vinci Surgical System Emerges
The 2000s witnessed a watershed moment with the introduction of the Da Vinci Surgical System . Developed by Intuitive Surgical, the Da Vinci System made its debut in 2000 and gained FDA approval for general laparoscopic surgery in 2001. This robotic platform allowed surgeons to perform minimally invasive procedures with enhanced precision and control.
Mid-2000s: Expanding Applications and Specialties
As the Da Vinci Surgical System gained popularity, its applications expanded beyond urology and gynecology to include cardiac, colorectal, and head and neck surgeries. Surgeons embraced the system for its 3D visualization, wristed instrumentation, and intuitive control, leading to a surge in robotic-assisted procedures.
2010s: Continued Advancements and Diverse Platforms
The 2010s saw a proliferation of robotic platforms catering to various medical specialties. Companies like Medtronic, Stryker, and Verb Surgical (a collaboration between Google and Johnson & Johnson) entered the arena, contributing to the diversification of robotic-assisted surgical options. Innovations extended to robotic exoskeletons for rehabilitation and telepresence robots for remote medical consultations.
Present Day: Robotic Integration and Future Prospects
In the present day, medical robotics has become an integral part of modern healthcare. The journey that began with visionary ideas and early experiments has evolved into a dynamic field where robots assist, collaborate, and enhance the capabilities of healthcare professionals. Surgical robots, rehabilitation robots, and telemedicine technologies continue to advance, promising a future where medical robotics plays a pivotal role in patient care, research, and education.
Future Horizons: AI, Telesurgery, and Beyond
Looking ahead, the future of medical robotics holds exciting possibilities. Artificial intelligence (AI) is poised to play a more significant role in guiding robotic systems, enhancing their decision-making capabilities. Telesurgery, where surgeons can perform procedures remotely using robotic systems, represents a frontier that holds promise for global collaboration and access to expertise.
In conclusion, the history of medical robotics is a narrative of innovation, collaboration, and a relentless pursuit of improving healthcare outcomes. From the untimely visions of pioneers to the assorted collection of robotic systems in use today, the journey reflects a commitment to pushing the boundaries of what is feasible in the intersection of technology and medicine. As the field continues to grow, the history of medical robotics serves as a proof to the transformative power of human cleverness in the service of curing.





