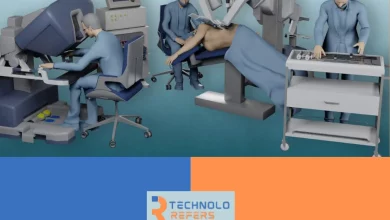
In the ever-evolving landscape of medical advancements, minimally invasive robotic surgery stands out as a beacon of progress, offering patients and medical professionals a transformative approach to surgical procedures. This cutting-edge technology has revolutionized the field of surgery, providing enhanced precision, shorter recovery times, and reduced scarring. As we delve into the realm of minimally invasive robotic surgery, we will explore its benefits, the risks associated with this innovative technique, and the devices that make it all possible.

Understanding Minimally Invasive Surgical Devices
Minimally invasive surgical devices are instruments designed to perform surgeries through small incisions or natural body openings, minimizing trauma to surrounding tissues. These devices play a pivotal role in various surgical procedures, including those utilizing robotic assistance. In the context of robotic surgery, these devices act as the extended hands of skilled surgeons, allowing them to perform complex procedures with greater control and accuracy.
One of the key components of minimally invasive robotic surgery is the robotic surgical system itself. These systems typically consist of a console where the surgeon sits, a robotic cart housing the mechanical arms, and a high-definition 3D vision system. The surgeon controls the robotic arms from the console, manipulating miniature instruments with incredible precision.
Examples of Robotic Surgery
- da Vinci Surgical System: Among the most well-known robotic surgical systems is the da Vinci Surgical System. Developed by Intuitive Surgical, this system has been used for a wide range of procedures, including prostatectomies, hysterectomies, and colorectal surgeries. The da Vinci System provides surgeons with a magnified, three-dimensional view of the surgical site, allowing for unparalleled precision.
- Mazor X Robotic Guidance System: Primarily utilized in spine surgeries, the Mazor X Robotic Guidance System assists surgeons in planning and executing procedures with utmost accuracy. This system uses preoperative imaging data to create a surgical blueprint, enabling the robot to guide the surgeon to the precise location for optimal results.
- Medtronic’s Hugo™ Surgical Robot: A more recent addition to the robotic surgery landscape, Medtronic’s Hugo™ Surgical Robot offers a modular and portable system designed for minimally invasive procedures. With advanced features like haptic feedback and artificial intelligence integration, the Hugo™ Surgical Robot aims to enhance the surgeon’s capabilities and improve patient outcomes.
Benefits of Minimally Invasive Robotic Surgery
- Precision and Accuracy: The robotic arms used in minimally invasive surgery can mimic the movements of a surgeon with exceptional precision. This level of accuracy allows for delicate procedures in areas that might be challenging to access using traditional methods.
- Reduced Blood Loss and Scarring: Smaller incisions result in reduced blood loss during surgery. Additionally, the minimal invasiveness of robotic procedures often leads to smaller scars or, in some cases, no visible scarring at all. This aesthetic advantage is particularly appealing to patients.
- Faster Recovery Times: Compared to traditional open surgeries, patients undergoing minimally invasive robotic procedures generally experience faster recovery times. This is attributed to the reduced trauma to surrounding tissues and the body’s ability to heal more efficiently.
- Enhanced 3D Visualization: The high-definition 3D vision systems in robotic surgical platforms provide surgeons with an immersive view of the operating field. This depth of visualization contributes to improved decision-making and maneuverability during surgery.
Risks of Robotic Surgery
While minimally invasive robotic surgery offers numerous advantages, it is essential to acknowledge and understand the potential risks associated with this advanced technology.
- Technical Failures: Robotic surgical systems are intricate machines, and technical malfunctions can occur. While such instances are rare, they have the potential to disrupt a surgery and necessitate a switch to traditional methods.
- Surgeon Learning Curve: Operating a robotic system requires specialized training, and surgeons may face a learning curve when transitioning from traditional methods to robotic-assisted procedures. During this phase, there is a risk of procedural errors.
- Cost Implications: The initial costs associated with acquiring and maintaining robotic surgical systems can be significant. This may result in higher overall healthcare expenses, which could impact accessibility to these advanced procedures.
- Lack of Tactile Feedback: One of the limitations of robotic surgery is the absence of tactile feedback for the surgeon. The inability to feel tissue resistance can potentially lead to inadvertent damage to delicate structures.
Disadvantages of Minimally Invasive Robotic Surgery
- High Initial Costs: The installation and maintenance of robotic surgical systems come with a hefty price tag. This initial investment can be a barrier for many healthcare facilities, limiting access to this technology in certain regions or for specific patient populations.
- Limited Availability: Due to the specialized training required to operate robotic systems, not all surgeons are proficient in using this technology. As a result, the availability of robotic-assisted procedures may be limited, particularly in smaller healthcare institutions.
- Dependency on Technology: In the event of technical issues or system failures, the dependency on robotic technology can pose a challenge. Surgeons must be prepared to switch seamlessly to traditional methods to ensure patient safety.
- Procedural Time: While the precision of robotic surgery is commendable, the setup and calibration of the system, as well as the learning curve for surgeons, can contribute to longer procedural times compared to traditional methods.
Conclusion
Minimally invasive robotic surgery represents a remarkable leap forward in the realm of medical innovation. The benefits it offers in terms of precision, reduced recovery times, and minimal scarring are undeniable. As technology continues to advance, the limitations and risks associated with robotic surgery are being addressed and mitigated.
While the disadvantages, such as high initial costs and a learning curve for surgeons, should be acknowledged, the potential for improved patient outcomes and the continued evolution of these technologies make minimally invasive robotic surgery an exciting and promising field. As researchers and practitioners work collaboratively to refine and expand the applications of robotic surgical systems, it is clear that the future of surgery is intricately tied to the further development of these cutting-edge technologies.
-
Applications Across Specialties:
Minimally invasive robotic surgery finds applications across various medical specialties, including urology, gynecology, cardiology, and general surgery. In urology, for example, robotic systems are commonly used for prostatectomies and kidney surgeries. Gynecologists utilize them for hysterectomies and other procedures. The versatility of robotic systems allows surgeons to address a wide range of medical conditions with precision.
-
Remote Surgery and Telepresence:
One of the futuristic aspects of minimally invasive robotic surgery is the potential for remote surgery. Telepresence capabilities in robotic systems enable surgeons to operate on patients located in different geographical areas. This technology has the potential to improve access to specialized surgical care, especially in rural or underserved areas where experienced surgeons may be scarce.
-
Integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI):
The integration of artificial intelligence into robotic surgical systems is a burgeoning area of research. AI algorithms can assist surgeons by analyzing real-time data, providing predictive analytics, and enhancing decision-making during surgery. This synergy between robotic technology and AI has the potential to further improve surgical outcomes and streamline procedures.
-
Single-Incision Robotic Surgery:
Single-incision robotic surgery takes the minimally invasive approach to the next level by performing surgeries through a single-entry point, often hidden within the navel. This technique aims to further reduce scarring and enhance cosmetic outcomes. While still in the early stages of adoption, single-incision robotic surgery holds promise for procedures across different specialties.
-
Pediatric Robotic Surgery:
Robotic surgery is not limited to adult patients; it has also found applications in pediatric surgery. The precision and minimally invasive nature of robotic systems make them suitable for delicate procedures in children. Pediatric urology, thoracic surgery, and gastrointestinal surgeries are among the areas where robotic technology is making a positive impact on young patients.
-
Training and Simulation:
As the use of robotic surgery grows, training programs and simulation technologies become crucial. Surgeons need to acquire the skills to operate these sophisticated systems effectively. Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) simulations are being developed to provide surgeons with a realistic training environment, allowing them to practice and refine their robotic surgical skills before entering the operating room.
-
Patient Education and Informed Consent:
With the rise of robotic surgery, patient education and informed consent become paramount. It is essential for healthcare professionals to communicate the benefits and potential risks of robotic procedures to patients, ensuring they have a clear understanding of what to expect. Educating patients on the technology, its advantages, and any associated limitations fosters trust and informed decision-making.
-
Global Accessibility:
Despite its numerous advantages, the accessibility of minimally invasive robotic surgery remains a challenge in some parts of the world. Factors such as cost, infrastructure, and training opportunities contribute to disparities in access. Efforts to make this technology more globally accessible involve collaborations between industry leaders, healthcare organizations, and policymakers to address these barriers.
-
Postoperative Care and Follow-up:
The postoperative care of patients who undergo minimally invasive robotic surgery is a crucial aspect of the overall treatment process. Understanding the specific recovery needs of patients, monitoring for any potential complications, and providing appropriate follow-up care contribute to the success of these procedures. Postoperative care protocols are continually evolving as more data becomes available.
-
Ethical Considerations and Patient Privacy:
As robotic surgery advances, ethical considerations come to the forefront. Issues such as patient privacy during remote surgeries, data security, and the ethical use of AI in surgical decision-making require careful consideration. Ensuring that patient rights and confidentiality are protected in the age of robotic surgery is an ongoing conversation within the medical and ethical communities.
In conclusion, the world of minimally invasive robotic surgery is vast and continually evolving. From innovative applications across medical specialties to the integration of artificial intelligence and the quest for global accessibility, the landscape of robotic surgery holds immense potential for improving patient outcomes and reshaping the future of surgical practice. As technology progresses and researchers delve deeper into these realms, the horizon for minimally invasive robotic surgery seems boundless.